This post provides a quick overview of the steps necessary to apply the MVVM pattern in a Kotlin Multiplatform application.
The starting point is a freshly downloaded project template from the Kotlin Multiplatform Wizard.

This post does not explain what MVVM is or discuss its pros and cons. Its main purpose is to serve as a concise note on the steps I take in a fresh project whenever I need this pattern.
The result of this post is a simple application that displays a counter. The user can start and stop the counter by pressing the corresponding buttons.
This is how it will look.
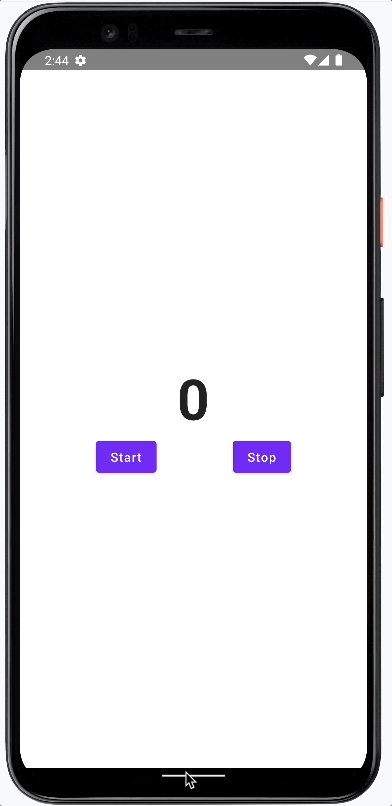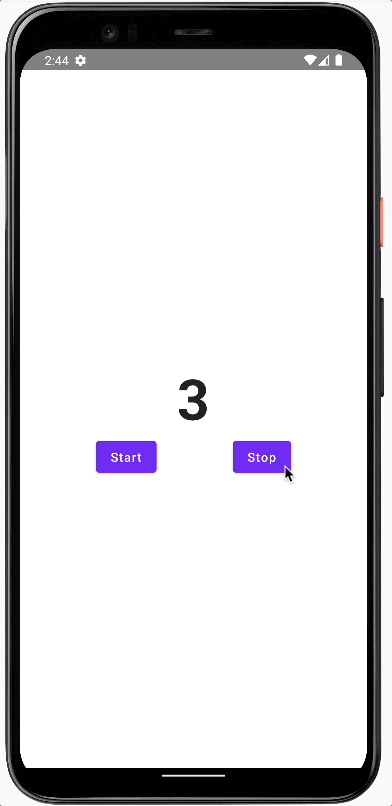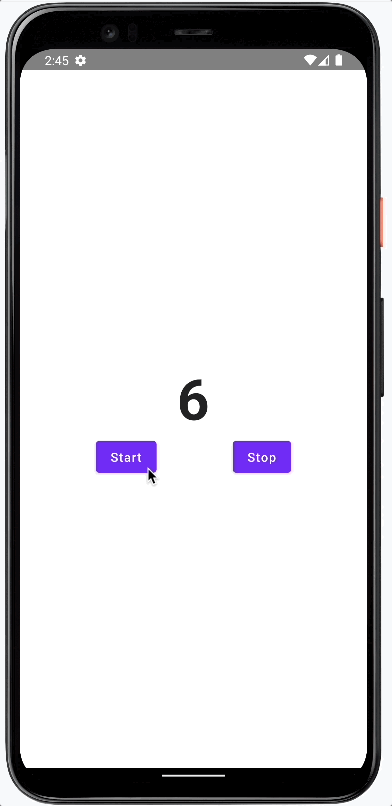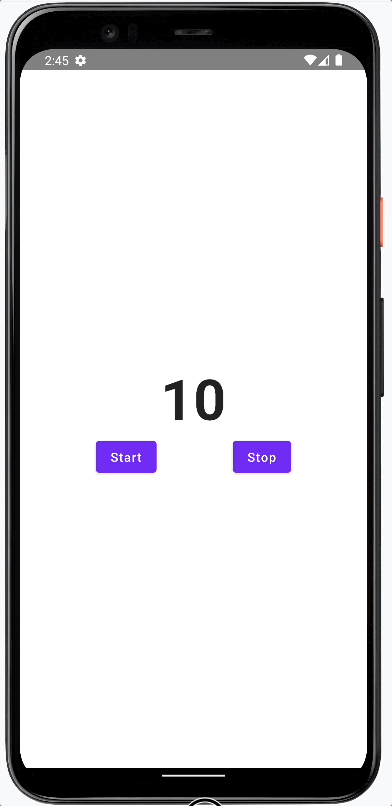
We follow a bottom-up approach and will add or modify these parts of the app:
- Gradle Dependencies
- States and Events
- Repository
- View-Model
- View
- Application
Gradle Dependencies
For my multiplatform projects I use MOKO MVVM.
In gradle/libs.versions.toml, add the required version and modules.
[versions]
mvvm = "0.16.1"
[libraries]
mvvm-compose = { module = "dev.icerock.moko:mvvm-compose", version.ref = "mvvm" }
mvvm-core = { module = "dev.icerock.moko:mvvm-core", version.ref = "mvvm" }Then reference the dependencies in composeApp/build.gradle.kts.
kotlin {
androidTarget {
compilations.all {
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "17"
}
}
}
sourceSets {
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation(libs.mvvm.core)
implementation(libs.mvvm.compose)
}
}
}
android {
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
}
}States and Events
The view and the view model communicate solely through states and events.
Create the state in composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin/NumberState.kt.
data class NumberState(
val number: Int
)Add the event in composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin/NumberEvent.kt.
sealed class NumberEvent {
object Start: NumberEvent()
object Stop: NumberEvent()
}Repository
Data comes from the repository created in composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin/NumberRepository.kt.
import kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchers
import kotlinx.coroutines.Job
import kotlinx.coroutines.delay
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.asStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class NumberRepository {
private val _number = MutableStateFlow(0)
val number = _number.asStateFlow()
private var job: Job? = null
fun start() {
job = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
while (true) {
delay(1000)
_number.value += 1
}
}
}
fun stop() {
job?.cancel()
}
}View Model
Create the view model in composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin/NumberViewModel.kt.
import dev.icerock.moko.mvvm.viewmodel.ViewModel
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.asStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.update
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class NumberViewModel(val repository: NumberRepository): ViewModel() {
val _state = MutableStateFlow(NumberState(0))
val state = _state.asStateFlow()
init {
viewModelScope.launch {
repository.number.collect { newNumber ->
_state.update {
it.copy(number = newNumber)
}
}
}
}
fun onEvent(event: NumberEvent) {
when (event) {
NumberEvent.Start -> repository.start()
NumberEvent.Stop -> repository.stop()
}
}
}View
As the second-to-last step, create the view in composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin/NumberView.kt.
@Composable
fun NumberView(state: NumberState, onEvent: (NumberEvent) -> Unit) {
Column(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Column {
Text(
text = "${state.number}", fontSize = 64.sp, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold
)
}
Row(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceEvenly
) {
Button(onClick = { onEvent(NumberEvent.Start) }) {
Text("Start")
}
Button(onClick = { onEvent(NumberEvent.Stop) }) {
Text("Stop")
}
}
}
}Application
Finally, wire everything up in the top-level App composable: composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin/App.kt
import androidx.compose.material.MaterialTheme
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.collectAsState
import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue
import dev.icerock.moko.mvvm.compose.getViewModel
import dev.icerock.moko.mvvm.compose.viewModelFactory
import org.jetbrains.compose.resources.ExperimentalResourceApi
@Composable
fun App() {
MaterialTheme {
val numberRepository = NumberRepository()
val numberViewModel = getViewModel(
Unit,
viewModelFactory { NumberViewModel(numberRepository) }
)
val state by numberViewModel.state.collectAsState()
NumberView(state, numberViewModel::onEvent)
}
}That’s it— the out-of-the-box multiplatform project template has been extended with an MVVM pattern that you can customize and extend as needed.